Do you want to know how to update or insert a new record using Spring Boot?
This article is for you.
Let's imagine the following scenarios:
We have an existing customer who wants to amend his phone number because it was wrong.
We have an entirely new customer who wants to register his details.
In one of my previous articles on How To Create A Spring Boot REST API, we have the following method:
public Customer saveCustomer(Customer savedCustomer) {
Customer customer = new Customer();
customer.setFirstName(savedCustomer.getFirstName());
customer.setLastName(savedCustomer.getLastName());
customer.setEmail(savedCustomer.getEmail());
customer.setPhoneNumber(savedCustomer.getPhoneNumber());
return customerRepository.save(savedCustomer);
}
The method above only covers scenario number 2.
We can refactor this method to perform an upsert operation.
1. What is an upsert operation?
An upsert operation is a database operation where you update an existing row if the value is already present. Otherwise, you save the new value into a new row.
2. How do you do an upsert?
To do this, you have to:
Delete any duplicate entry from the Customer table to avoid the
1062 - Duplicate Entry error.Use the email to identify a customer uniquely. Therefore, make the
emailcolumn unique.
ALTER TABLE customer ADD UNIQUE (email);
- Refactor
save()method logic so that it checks if an entry exists in the database. If it does, update the existing entry. Otherwise, create a new one and insert it into the database.
public Customer saveCustomer(Customer savedCustomer) {
Customer customer = customerRepository
.findCustomerByEmail(savedCustomer.getEmail());
if(customer != null) {
customer.setFirstName(savedCustomer.getFirstName());
customer.setLastName(savedCustomer.getLastName());
customer.setPhoneNumber(savedCustomer.getPhoneNumber());
} else {
customer = new Customer();
customer.setFirstName(savedCustomer.getFirstName());
customer.setLastName(savedCustomer.getLastName());
customer.setEmail(savedCustomer.getEmail());
customer.setPhoneNumber(savedCustomer.getPhoneNumber());
}
return customerRepository.save(customer);
}
public Optional<Customer> getCustomerByEmail(String email){
Customer customer = customerRepository.findCustomerByEmail(email);
return Optional.ofNullable(customer);
}
3. Testing on Postman
Let's test this logic via Postman:
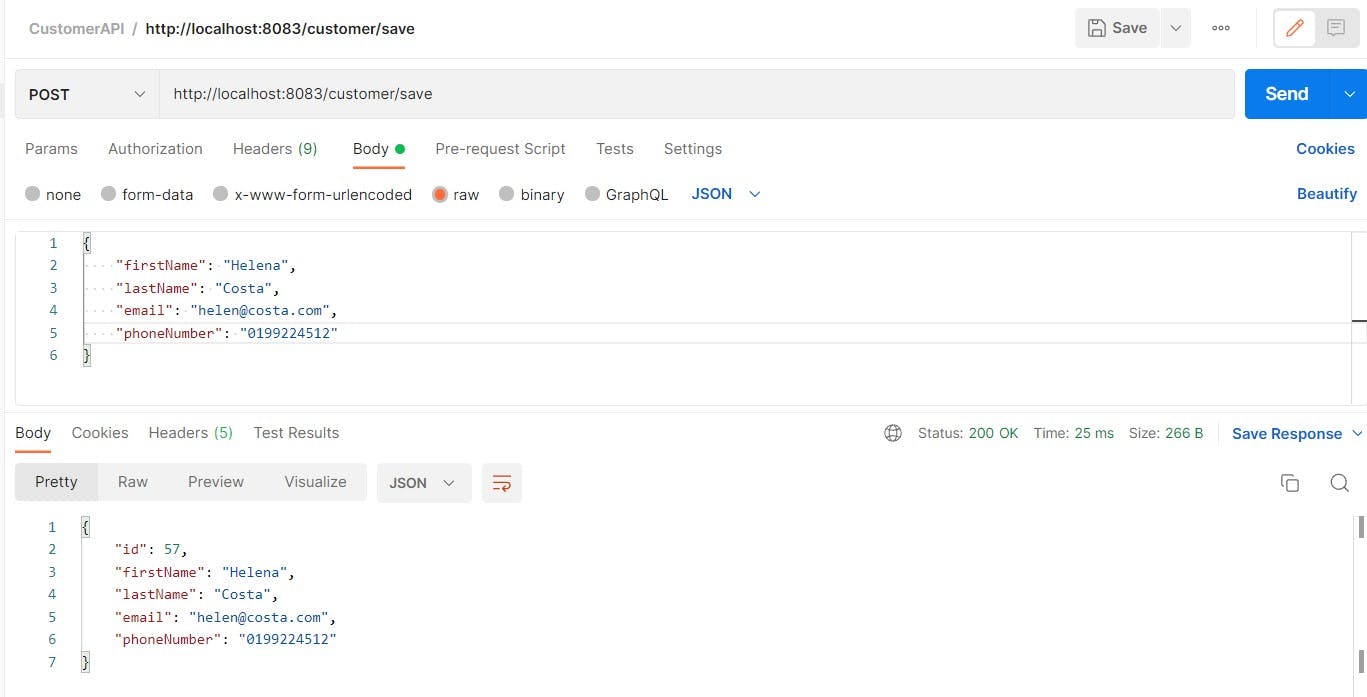
The record gets updated in the database too.
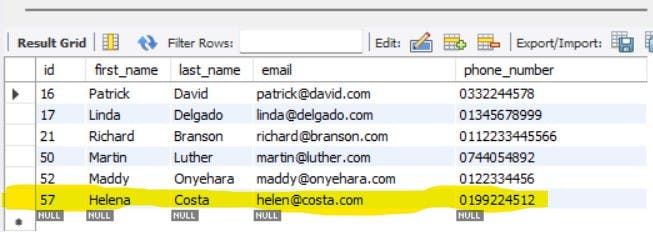
Now, let's try to update Helena's phone number with a different one.
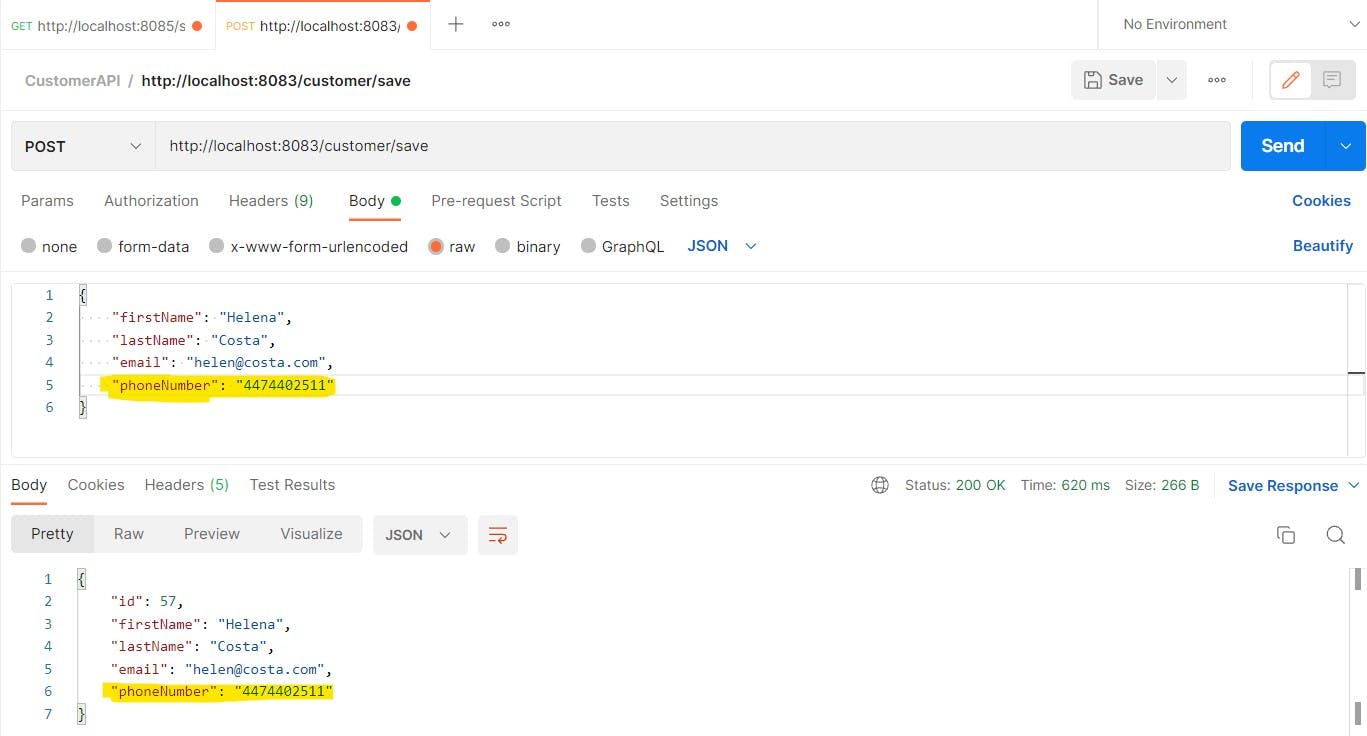
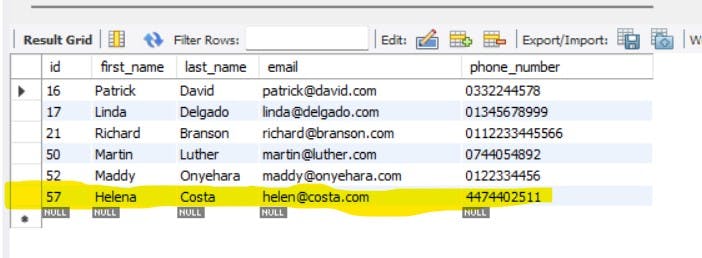
In the database, Helena's phone number should be updated (no new row should be created).
Key Takeaways
After reading this article, you know what an upsert operation is, how to do an upsert and how to test an upsert using Postman.
If this article was helpful to you, I invite you to subscribe to my FREE weekly newsletter, where I share insights on software engineering, career development, etc.
Until next time!
🙋🏾♀️

